
|
| No dimensional drawings!
Unit:
|

|
| No dimensional drawings!
Unit:
|
3 技术要求
3.1 材料
自钻自攻螺钉应使用渗碳钢或热处理钢制造。
3.2 金相性能
3.2.1 表面硬度
热处理后自钻自攻螺钉的表面硬度应≥530HV0.3。
3.2.2 芯部硬度
热处理后的芯部硬度为:
——320HV5~400HV5 用于螺纹规格≤ST4.2;
——320HV10~400HV10 用于螺纹规格>ST4.2。
推荐的最低回火温度为330℃。
应避免275~315℃的回火温度范围,以便将回火马氏体脆断风险减少到最低程度。
3.2.3 渗碳层深度
渗碳层深度应符合表1给出的数值。
表1 渗碳层深度
螺纹规格 | 渗碳层深度 | |
min | max | |
ST2.9和ST3.5 | 0.05 | 0.18 |
ST4.2~ST5.5 | 0.10 | 0.23 |
ST6.3 | 0.15 | 0.28 |
3.2.4 显微组织
在热处理后自钻自攻螺钉的显微组织中,表面硬化层和芯部之间不应出现带状铁素体。
3.2.5 氢脆
电镀自钻自攻螺钉存在因氢脆而断裂的危险。因此,应由制造者和(或)电镀者采取措施,包括按GB/T 3098.17 进行试验检查,以控制该危险的发生。
GB/T5267.1中有关电镀紧固件消除氢脆的测量要求,也应予以考虑。
3.3 机械性能
3.3.1 钻孔性能
螺钉钻削部分应能在4.2.1规定的试验条件下,钻出为挤压与螺钉配合的内螺纹所需要的预制孔。
3.3.2 螺纹成型性能
在按3.3.1钻出的预制孔中,自钻自攻螺钉应能挤压出与其配合的内螺纹,并在拧入4.2.1.1规定的试验板时,螺钉螺纹无变形。
3.3.3 扭转强度
按4.2.3规定的试验方法对自钻自攻螺钉进行试验时,其扭转强度应能保证螺钉的破坏扭矩值等于或大于表4的规定。
4 试验方法
4.1 金相性能试验
4.1.1 表面硬度试验
表面硬度试验按GB/T 4340.1规定。压痕尽可能在平面部分,并优先在螺钉头部。
4.1.2 芯部硬度试验
芯部硬度试验按GB/T 4340.1规定,并应在横向显微截面上进行。
4.1.3 渗碳层深度测定
表面渗碳层深度应采用显微镜在纵向显微截面上,牙顶与牙底中间部分的牙侧处进行,或对≤ ST4.2的螺钉在螺纹牙底处进行测定。
仲裁试验,应在金相试件的螺纹轮廓上用试验力为300 g的显微维氏硬度进行。渗碳层深度应自超过芯部实际硬度30HV的点起计算。
4.1.4 显微组织试验
显微组织试验应按相应金相检验标准进行。
4.2 机械性能试验
4.2.1 钻孔和攻丝试验
4.2.1.1 试验装置
图1 为试验装置示例。
试验板应由含碳量≤0.23%的低碳钢制成,其硬度为110HV30~165HV30(按GB/T4340.1测定)。试验板的厚度应符合表2规定。
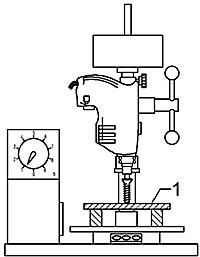
1—试验板
图1 钻孔和攻丝试验装置
表2 钻孔和攻丝试验数据
螺纹规格 | 试验板厚度1)/mm | 轴向力/N | 拧入时间/S max | 载荷下螺钉转速/mm -1 |
|
ST2.9 | 0.7+0.7=1.4 | 150 | 3 | 1800~2500 |
|
ST3.5 | 1+1=2 | 150 | 4 | 1800~2500 |
|
ST4.2 | 1.5+1.5=3 | 250 | 5 | 1800~2500 |
|
ST4.8 | 2+2=4 | 250 | 7 | 1800~2500 |
|
ST5.5 | 2+3=5 | 350 | 11 | 1000~1800 |
|
ST6.3 | 2+3=5 | 350 | 13 | 1000~1800 |
|
1) 试验板厚度可以由两块钢板组成。这些数值仅适用于验收检查。 | |||||
4.2.1.2试验程序
将有镀层或无镀层的(按使用要求)螺钉试件拧入试验板,直至有一扣完整螺纹穿过试验板。
表2规定的轴向力和螺钉转速适用于钻孔和攻丝过程。
4.2.2 钻孔检验
需经双方协议,可进行钻孔检验。为此,所使用的试验板应符合4.2.1.1的要求,其厚度应符合表3规定。试验板上钻孔的部分,应先冲出定位点。钻透试验板后,钻孔的最大尺寸应不超出表3规定的极限。
图2的试验夹具是对图1试验装置的补充。套简内径应比螺纹大径约加大0. 25 mm。套筒长度的选择应使钻头部分能伸出套筒。
表2规定的轴向力也可用于指导安装自钻自攻螺钉。如果超过这些数值,该钻头部分可能因断裂或过烧产生局部损坏。
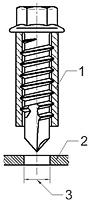
1—套筒;2—试验板;3—钻孔
图2 钻孔试验夹具
表3 钻孔试验数据
螺纹规格 | 板的厚度 | 孔径 | |
min | max | ||
ST2.9 | 1 | 2.2 | 2.5 |
ST3.5 | 1 | 2.7 | 3.0 |
ST4.2 | 2 | 3.2 | 3.6 |
ST4.8 | 2 | 3.7 | 4.2 |
ST5.5 | 2 | 4.2 | 4.8 |
ST6.3 | 2 | 4.8 | 5.4 |
4.2.3 扭矩试验
螺钉试件应夹紧在与螺钉螺纹相匹配的螺纹开合模或其他装置内,螺钉夹紧部分不应损伤。
图3为试验装置示例。夹紧后,至少有两扣完整螺纹伸出夹紧装置,除螺钉钻头部分外至少有两扣完整螺纹牢固地夹紧在开合模内。在螺钉短规格的情况下,应牢固地夹紧整个螺纹,但螺钉头部不应承受夹紧力。
用经标定的扭矩—测量装置,对螺钉施加扭矩直至断裂。螺钉应符合表4规定的破坏扭矩。
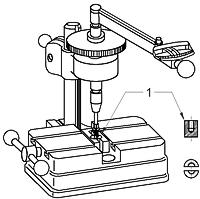
1—带自攻螺纹的盲孔开合模
图3扭矩试验装置
表4 破坏扭矩
螺纹规格 | 破坏扭矩 min |
ST2.9 | 1.5 |
ST3.5 | 2.8 |
ST4.2 | 4.7 |
ST4.8 | 6.9 |
ST5.5 | 10.4 |
ST6.3 | 16.9 |
用于扭矩试验的扭力扳手,测量误差应在规定扭矩值的±3%以内。也可使用能显示扭矩且精度相当的动力装置。
仲裁试验时应使用手动扭力扳手。
Mechanical properties of fasteners - Stainless steel Bolts, screws and studs
Mechanical properties of fasteners-Stainless steel and nickel alloys bolts, screws, studs and nuts for high temperature applications
Mechanical properties of fasteners-Guidance for the selection of stainless steels and nickel alloys for fasteners
Mechanical Properties of Fasteners - Prevailing Torque Type Steel Nuts
Mechanical properties of fasteners-Set screws

Mechanical properties of fasteners-nuts with coarse thread
High-strength structural bolting assemblies for preloading - Part2: Suitability for preloading

Mechanical properties of fasteners - Stainless steel nuts

Mechanical properties of fasteners - Stainless steel set screws


Mechanical properties of fasteners - Stainless steel Bolts, screws and studs

Mechanical properties of fasteners-Bolts、screws and studs
Mechanical properties of fasteners Parts for bolted connections for use at temperatures from -200 ℃~+700 ℃

Mechanical properties of fasteners made of the fine grain non-heat treatment steel-Bolts,screws and studs

Spring washer technical conditions


Mechanical properties of fasteners-Blind rivets

Mechanical properties of fasteners. Wing nuts with specified proof torque

Mechanical properties of fasteners. Prevailing torque type steel hexagon nuts

Mechanical properties of fasteners-Nuts-Fine pitch thread

Mechanical propretles of fasteners tapping screws

Mechanical properties of fasteners-Bolts、screws and studs made of stainless-steel

Machanical properties of fasteners-Thread rolling screws
Mechanical properties of fasteners Bolts,scrows,studs and nuts made of non-ferrous metals

Specification for revit
Mechanical Properties of Fasteners 一 Tapping Screws
Fasteners - Mechanical properties of corrosion-resistant stainless steel fasteners - Part 7: Flat washers with specified grades and property classes
Heat treated tapping screws - Mechanical and physical properties
Mechanical properties of fasteners made of carbon steel and alloy steel — Part 2: Nuts with specified property classes
Mechanical properties of corrosion-resistant stainless steel fasteners - Nuts with specified grades and property classes bsi.
Mechanical properties of fasteners made of carbon steel and alloy steel – Part 3: Flat washers with specified property classes
Mechanical Properties of Fasteners - Prevailing Torque Type Steel Nuts

Mechanical properties of fasteners made of carbon steel and alloy steel. Part 1:Bolts,screws and studs with specified property classes. Coarse thread

Mechanical properties of fasteners made of carbon steel and alloy steel - Part 2: Nuts with specifed property classes - Coarse thread and fne pitch thread

Mechanical properties—Set screw and similar threaded fasteners with specified hardness classes

Heat-treated steel tapping screws - Mechanical properties

Mechanical properties of corrosion resistant stainless steel fasteners—Part 1:Nuts

Mechanical properties of corrosion resistant stainless steel fasteners— Part 3:Set screws and similar fasteners not under tensile stress

Mechanical properties of corrosion resistant stainless steel fasteners— Part 4:Tapping screws

Drilling screws with tapping screw thread— Mechanical and functional properties

Mechanical and performance requirements of case hardened and tempered metric thread rolling screws
Mechanical properties of fasteners - Part 6: Nuts with specified proof load values - Fine pitch thread

Torsional test and minimum torques for bolts and screws

Mechanical properties of fasteners—Bolts,screws,studs and nuts made of non-ferrous metals
Heat-treated steel tapping screws - Mechanical properties
Test methods of tightening torque for bolts
Maximum Drive Torque for Type TRS Tapping Screws
Torsional Strength Requirements for Tapping Screws
Nylon Insert Locknuts (Inch Series)
Aerospace series - Bolts, MJ threads, in heat resisting steel FE-PA2601 (A286) - Classification: 900 MPa (at ambient temperature)/650℃ - Technical specification
Non-preloaded structural bolting assemblies - Part 1: General requirements
High-strength structural bolting assemblies for preloading - Part 2: Suitability for preloading
Mechanical properties of fasteners - Part 7: Torsional test and minimum torques for bolts and screws with nominal diameters 1 mm to 10 mm
Mechanical properties of fasteners - Part 2: Nuts with specified proof load values - Coarse thread
Mechanical properties of fasteners - Part 6: Nuts with specified proof load values - Fine pitch thread
Mechanical properties of fasteners - Part 1: Bolts, screws and studs
Mechanical Properties of Fasteners - Bolts, Screws, Studs and Nuts

Suppliers(1)
Carbon Steel Bolts, Studs, and Threaded Rod 6000 PSI Tensile Strength
Carbon steels、alloy steels and stainless materials for bolts and nuts
Mechanical properties of fasteners made of carbon steel and alloy steel Part 2: Nuts with specified property classes - Coarse thread and fine pitch thread
Mechanical properties of fasteners made of carbon steel and alloy steel. Part 1:Bolts,screws and studs
Self-drilling screws for the building and construction industries Part 1: General requirements and mechanical properties
Thread Rolling Screws
Maximum Drive Torque for Type TRS Tapping Screws
Torsional Strength Requirements for Tapping Screws
