|
|
| No dimensional drawings!
Unit:
|
|
|
| No dimensional drawings!
Unit:
|
一、技术要求
主要指标
1.螺栓的机械性能分级按表1的规定。
表1
级别(标记) | 3.6 | 4.6 | 4.9 | 5.6 | 5.9 | 6.6 | 6.9 | 8.8 | 10.9 | 12.9 | |
抗拉强度σb min kgf/mm2 | 33 | 40 | 50 | 60 | 80 | 100 | 120 | ||||
屈服极限σs min kgf/mm2 | 18 | 24 | 36 | 30 | 45 | 36 | 54 | 64 | 90 | 108 | |
伸长率 % | δ5≥ | 25 | 20 | / | 20 | / | 16 | / | 12 | 9 | 8 |
δ1.8≥ | / | 30 | 10 | 30 | 10 | 24 | 10 | 15 | 13 | 12 | |
硬度 HB | 90~ | 110~ | 145~216 | 175~255 | 230~305 | 295~375 | 355~430 | ||||
推荐材料牌号 (大量生产) | 10 A2 | 15 A3 | 10 A2 | 25 35 | 15 A3 | 45 | 35 | 35 45 | 40Cr15MnVB | 30CrMnSi15MnVB | |
头杆结合强度试验 | 对不经热处理的冷镦螺栓,需进行本项试验。 试验后支承面与螺杆交接处,不允许有裂缝。 | ||||||||||
注:① 在一般情况下,伸长率和屈服极限只作为参考指标,由制造厂在生产工艺中控制。如用户要求考核屈服极限和伸长率时,应在订单中注明;
② 10.9、12.9级的硬度范围分别相应于铬钢、铬锰硅钢。选用其他材料,与强度相对应的硬度按 GB 1172—74 的规定。
2. 螺拴机械性能分级的标记;
(1)标记由数字表示,笫一位数字为 σb min / 10,带小数点的第二位数字为屈强比(σs min /σb min );
(2)按机械性能分级的螺栓,当d≥5mm和大于或等于4.6级时,应在产品上制出标记(与表1相同),但对相应尺寸标准的标记示例中允许省略机械性能标记的,并且小于或等于6.9级的螺栓,可不制出标记;
(3)标记应在头部顶面或凹穴底面上制出。可为凸字或凹字,其大小由制造厂规定。
3. 当机械性能分级的规定不能满足使用要求时,可按表2规定的材料选用。
表2
种类 | 牌号 | 标准编号 |
特种钢 | 1Cr13、2Cr13 Cr17Ni2 1Cr18Ni9Ti | GB 1220-75 |
铜及其合金 | H62、HPb59-1 H62防磁、HPb59-1防磁 | YB 457-71 |
铝及其合金 | LY8 LY10 |
|
注:① 不同冶炼及浇注方法制造的钢材同样可以采用。 ② “牌号”栏内每一通栏中所列各种材料,可以互相通用。 | ||
4. 螺栓上的螺纹:
(1)螺纹基本尺寸按 GB 196—63 的规定。螺纹公差按 GB 197—63 的规定;粗牙为2、3级;细牙为2、2a、3级,粗制螺拴仅按3级公差制造;
(2)螺纹侧面的光洁度按表3的规定。内、外径及螺尾和最初两扣的光洁度不作规定;
表3
类别 | 侧面光洁度 |
精制螺栓 | ▽5 |
粗制螺栓 | ▽3 |
注:当螺距(t)不大于0.5mm时,可不检查光洁度。 | |
(3)螺纹表面不允许有裂缝。
5. 支承面对螺杆轴心线的不垂直度(β)(图1):
精制螺栓:β≤1°;
粗制螺栓:β≤2°。
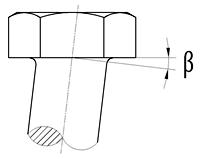
图1
6. 螺栓应进行不直度的检查。螺栓应顺利落入检验模。
7. 当用户提出要求时,可检查精制螺栓的杆部脱碳层:
对5.9级及其以下的脱碳层应小于直径的2.5%;
对6.6级及其以上的脱碳层应小于或等于直径的1.5%.
一般指标
8. 螺杆上无螺纹部分的直径:
(1) 精制等粗杆的螺栓,其允差按 GB 197—63 粗牙普通螺纹3级精度外径的规定;
(2) 螺纹如系辗制,允许制成细杆,即小于螺纹外径,其尺寸及允差由制造厂规定;
(3) 沉头、半圆头、导颈及活节螺栓的直径d2小于螺纹外径,其尺寸及允差由制造厂规定。
9. 螺纹空白:
注:螺纹空白系指螺杆上全部制出螺纹时,螺尾末端与支承面间(或与导颈、方颈末端间)的长度;或者铰制孔用螺栓的螺尾与螺杆上无螺纹部分末端间的长度。精制螺栓不大于1.5t;
粗制螺栓不大于2t。
t——粗牙螺纹螺距。
10. 螺杆上不全部制出螺纹,并采用辗制螺纹工艺制造等粗杆的螺栓时,其螺尾末端与无螺纹部分末端间,允许有不大于2t(t——粗牙螺纹螺距)的颈部(图2)。
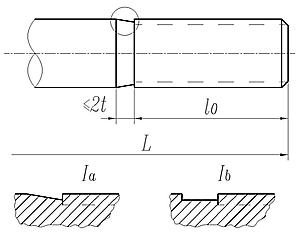
图2
11. 螺纹长度(L0)的允差:
当d≤5mm时,+3t;
d>5mm时,+2t;
t——粗牙螺纹螺距。
14. 带凹穴螺栓,其凹穴直径D2≈(0.8~0.9)S、深度h≈(0.2~0.3)H、凹穴底部允许制成凹球面。凹穴螺拴对角的圆钝应由生产工艺控制,即在距顶面寸1/3 H(头高)处,D的尺寸公差不大于9级(GB 159—59)、单向负偏差。12. 螺尾及退刀槽按 GB 3—58 的规定。
13. 精制螺栓的螺杆末端按 GB 2—76 的规定制成倒角或球面,采用辗制螺纹工艺或粗制螺栓,可制成平端,允许有自然形成的圆穴、不显著的压扁。螺杆末端允许留有中心孔。
15. 螺栓的顶圆直径(D1),顶面与侧面交换处的倒角桉图3的规定。
精制螺栓:D1≈0.95S;
粗制螺栓:D1≈0.9S。
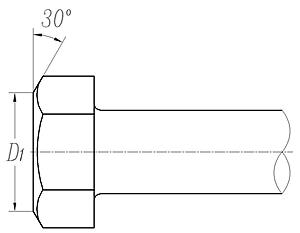
图3
16. 六角头和方头螺拴的头部侧面对支承面的不垂直度(γ)(图4):
精制螺栓:γ≤1°30';
粗制螺栓:γ≤2°。
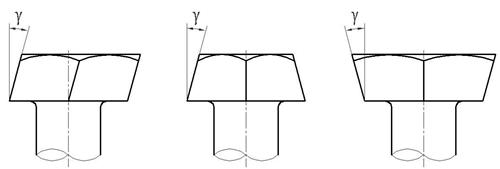
图4
17. 各种半圆头螺栓、螺栓方颈及导颈的末端,根据生产工艺的需要,允许按图5制造。
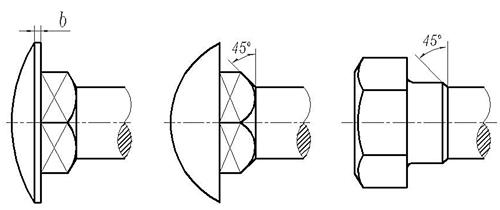
图5
18. 螺栓头对螺杆轴心线的不同轴度按表4的规定。
表4(mm)
d | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 | (14) | 16 | (18) | 20 | (22) | 24 | (27) | 30 | 36 | 42 | 48 | |
不同轴度 | 精制螺栓 | 0.20 | 0.25 | 0.30 | 0.40 | 0.45 | 0.60 | ||||||||||||
粗制螺栓 | / | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 1.0 | 1.2 | 1.4 | |||||||||
19. 头部带槽螺栓的槽对螺杆轴心线的不对称度按表5的规定。
表5(mm)
d | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 | (14) | 16 | (18) | 20 |
不对称度 | 0.15 | 0.25 | 0.30 | 0.35 | 0.45 | ||||||
20. 螺杆带孔螺拴的螺杆上孔的轴心线对螺杆轴心线的位移度按表6的规定。
表6(mm)
d | 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 | (14) | 16 | (18) | 20 | (22) | 24 | (27) | 30 | 36 | 42 | 48 |
位移度 | 0.20 | 0.25 | 0.30 | 0.45 | 0.50 | ||||||||||
21. 螺纹表面不允许有妨碍螺纹量规自由旋入的碰伤和毛刺;不允许有影响使用的双牙尖、划痕和扣不完整。
22. 螺拴表面不允许有影响使用的凹痕、毛刺、浮锈、圆钝、飞边、烧伤和氧化皮。精制螺拴不允许有浮锈和烧伤。在螺栓顶面30°倒角处不允许有影响使用的裂缝。
23. 在名称中未注明“粗制”的,均为精制螺栓。精制与粗制是按尺寸精度、表面光洁度及技术要求划分的,与生产工艺无关。
24. 上述规定以外的技术要求,由供需双方协议。
二、测试方法
25. 螺栓的硬度试验:
(1)一般可以硬度试验结果作为抗拉强度的验收依据。如有争议,应以抗拉强度试验结果为准;
(2)硬度试验部位,规定为螺杆末端。其试验方法按 GB 231—63 的规定;
26. 抗拉强度试验,在拉力试验机上进行;
(1)将螺栓拧上螺母(或带有内螺纹的专用夹具),再装入拉力试验机上进行试验(图6);
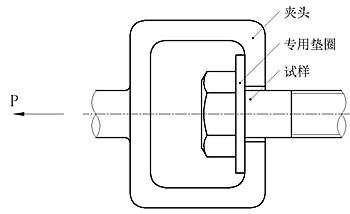
图6
(2) 试验中,当负荷达到σb min·A时,螺拴不得拉断,当负荷大于σb min·A直至拉新后,亦不允许在头部或支承面与螺杆交接处断裂;
σb min——按表1或表2原材料的最小抗拉强度极限。

式中:
d2——螺纹中径公称尺寸;
d1——螺纹内径公称尺寸;
H——螺纹三角形高度。
(3)对大规格螺栓的抗拉强度试验,根据设备条件,可以采取车削比例试祥进行。此时其伸长率按δ5,考核。
比例试样的型式、尺寸按图7的规定制取。
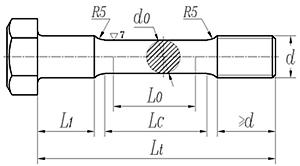
图7
图中:L0——5d0或5.65√A0;
A0——截面积;
d0——(3/4)d(螺纹直径)<d0<d1(螺纹内径);
Lc=L0+d0;
Lt=Lc+2R+(≥d)+L1。
其他技术要求按 GB 228—76《金属拉力试验法》的规定;
(4)对d≤5mm的螺栓,不进行抗拉强度试验;
(5)对较短规格的螺栓,可采用由相同条件制成的同一直径长规格的螺栓进行抗拉强度试验。
27. 屈服极限,在进行抗拉强度试验的同时求得。
28. 伸长率:用螺栓成品进行试验,在抗拉强度试验的同时求得,可按δ1.8或δ5考核。
(1)伸长率桉δ1.8考核时:

式中: L0≈1.8·d(螺纹内径);
L1——试验后的标距长度。
在试验时将L0转换为螺纹整数扣数进行测量,如表7。
表7
d(mm) | 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 14 | 16 | 18 | 20 | 22 | 24 | 27 | 30 |
拉力标距扣数 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 14 | ||||||||
注:本表适用于粗牙螺纹。 | ||||||||||||
(2) 伸长率按δ5 考核时:
当要求按δ5 考核伸长率时,其试样按图7制取。

式中, L0=5·d0;
L1——试验后的标距长度。
29. 头与螺杆结合强度试验——将螺栓装入带有15°斜面的检验模中,锤击螺栓头部,使支承面与斜面贴合。检验模及锤击位巨如图8~10所示。
(1)检验模的孔径:
精制螺栓按 GB 152—76 精装配的规定;
粗制螺栓按 GB 152—76 中等装配的规定。
(2)如螺杆上全部制出螺纹时,应在制出螺纹前或在试件上去除螺纹后进行试验。
当制出螺纹前进行试验时,检验模的孔径为螺纹公称尺寸与“间隙”之和;当去除螺纹后进行试验时,检验模的孔径为螺纹内径公称尺寸与“间隙”之和;
“间隙”为螺纹外径公称尺寸与本条第(1)款相应检验模孔径之差。
(3)头部带孔螺栓应在制出孔d4前进行试验;
(4)方颈螺栓和带榫螺栓的检验模如图9及图10所示。
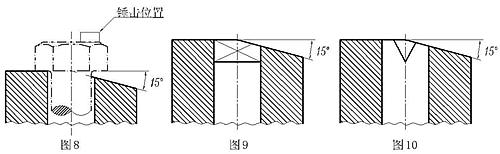
30. 螺纹检查——用螺纹量规和光滑极限量规(或万能量具)进行。
(1)对下列螺纹的检查, 仅用过端呈规和光滑极限昼规(或万能量具)进行:
粗牙2级、细牙2a级,t≤0.35mm;
粗牙3级、细牙3级,t≤0.8mm。
三、验收规则、包装与标记(2)止端螺纹量规的旋入量不允许大于3-1/2扣,但当螺纹在4扣以内时,也不允许止规全部通过。
(3)螺纹如系辗制,最初两扣外径不作检查。
31. 螺栓不直度检查——用检验模进行.
(1)采用检验模的孔径为:
精制螺栓 按GB 152—76 精装配的规定;
粗制螺栓 按GB 152—76 中等装配的规定。
(2)对精制螺栓,当用户在订单中提出要求时,应采用带螺纹的检验模。其无螺纹部分的孔径按GB 152—76 中等装配的规定,螺纹按GB 197—63 规定的3级精度。
(3)检验摸的高度不小于被检螺栓的长度。
(4)当螺杆长度L>10d或大于150mm时,亦可用平台及塞尺进行检查。螺杆与平台的最大间隙应不大于检验模孔公称直径与螺杆公称直径之差。
32. “放扳手处”尺寸(S)的检查——在最大尺寸部位进行。
33. 带凹穴螺拴对角尺寸(D)的检查——在距顶面1/3 H处,用专用卡板或万能量具进行。
34. 螺栓长度(L)的检查,以短边为准。
35. 验收规则、包装与标记按GB 90—76 的规定。
Specifications of high strength bolts with large hexagon head, large hexagon nuts, plain washers for steel structures
Self-tappingscrew connections - Specification ofthepilotholediameterand tighteningtorque
General specification for blind bulbed rivet
Composite sealing gasket material
Corrosion of metals and alloys - Corrosivity of atmospheres - Part 1 : Classification, determination and estimation
Corrosion of metals and alloys - Corrosivity of atmospheres - Part 2: Guiding values for the corrosivity categories
Steel wire ropes for general purposes
Specifications for spring washers - Conical spring washers
Specifications for retaining rings-Circlips
Hot formed helical compression springs - Technical Requirement
High-strength structural bolting assemblies for preloading - Part 1: General requirements
Cold coiled helical springs technical specifications - Part 1: Extension spring
Cold coiled helical springs technical specifications - Part 2: Compressions spring
Specification For Wire Thread Inserts
General specifications for packing of mechanical and electrical product

Fasteners - General requirements for bolts,screws,studs and nuts
24° Cone Connectors - Specification
Flared couplings - Specification
Specification of metallic ring-joint gaskets for steel pipe flanges
Specifications of high strength bolts with large hexagon head, large hexagon nuts, plain washers for steel structures
Specification of gauges for general purpose screw threads
Fasteners - Marking and packaging
Plain Washers for Bolts, Screws and Nuts - General Plan
Fasteners - Surface discontinuities - Bolts, screws and studs for general requirements
Fasteners-Surface discontinuities - Nuts
Fasteners - Surface discontinuities - Bolts, screws and studs for special requirements
Technical requirements for anchors
Specifications For Drive Rivets
Technical requirement for sets of torshear type high strength bolt hexagon nut and plain washer for steel structures
Specifications for parts and units of jigs and fixtures
Grease nipples and lubricating cups technical specification
Oil level indicators technical specification
Counterbores for hexagon socket head and slotted cheese head screws
Procurement Specification For Self-Locking Nuts
Specification for tab washer

Specifications for pins
Spcifications for ring - Cutting rings
Technical requirements of malleable cast iron pipe fittings
Fasteners - Part 27: Steel screws, bolts and studs made of steel with pre-adhesive coating - Technical specifications

metal washers; technical delivery conditions

Steel flat products; Hot rolled plate 3 to 150 mm thick; Permissible deviations of dimension, weight and form
Flat products of steel; cold rolled steel strip; dimensions, tolerances on dimensions and form.
Fasteners - Grooved pins - General requirements
Commercial vehicles - Wheel-hub attachment dimensions
Corrosion of metals and alloys - Corrosivity of atmospheres - Guiding values for the corrosivity categories
Tools for pressing - Elastomer pressure springs - Part 2: Specification of accessories
Hydraulic fluid power - Two-, three- and four-port screw-in cartridge valves - Cavities
Red Vulcanized Fibre Board Washer for Micro-Motor
Cold heading dies for fasteners - Specifications

Specification of Stamping Die Components
Specifications for parts and units of jigs and fixtures
Internal combustion engines - Cylinder head and flywheel nuts - Specifications
Timber structures - Dowel-type fasteners - Requirements
Aerospace series - Bolts, MJ threads, in heat resisting nickel base alloy NI-PH2601 (Inconel 718) - Classification: 1275 MPa (at ambient temperature)/650 °C - Technical specification
High-strength structural bolting assemblies for preloading - Part 1: General requirements
Flanges and their joints - Bolting - Part 3: Classification of bolt materials for steel flanges, class designated
Metallic products - Types of inspection documents
Flanges and their joints - bolting - Part 2: Classification of bolt materials for steel flanges, PN designated
Flanges and their joints - bolting - Part 1: Selection of bolting
Aerospace series - Inserts, screw thread, helical coil, self locking - Technical specification
Aerospace series - Inserts, screw thread, helical coil, self-locking - Assembly procedure
Specification for Selection of Steel Pipe Flanges , Gaskets and Bolting (PN designated)
Alloy and Carbon Steel Bolting for Use in the Petroleum and Natural Gas Industries
Standard Specification for Steel Transmission Tower Bolts, Zinc-Coated and Bare
Mechanical fixation component for waterproofing membrane roofing
Construction machinery and equipment Specification of high strength fasteners
Fastenersart - Standard - Cap Screws, Hex Bolts, and Hex Nuts
Steel Self-Drilling Tapping Screws
Technical conditions for threaded fasteners with adhesive coating-Part 1: Microencapsulated locking coating
Technical condions for threaded fasteners with adhesive coating-Part 2: Polyamlde locking coating
Technical Supply Conditions For Threaded Steel Fasteners - Part 1 General Requirements For Bolts, Screws And Studs
General data for machine screws and tapping screws
Plain nuts and slotted nuts - Part 1: General specification
Disc springs - Calculation
